Homodimerization of Cell Adhesion Protein CD44 Modulated by Palmitoylated Modifications and Membrane Environments
ID:52
Submission ID:39 View Protection:ATTENDEE
Updated Time:2021-08-03 19:13:27 Hits:1446
Poster Presentation
Abstract
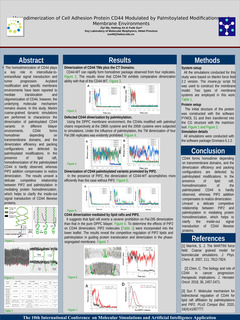
The homodimerization of CD44 plays a key role in intercellular-to-extracellular signal transduction and tumor progression. Acylated modification and specific membrane environments have been reported to mediate translocation and oligomerization of CD44, however, the underlying molecular mechanism remains elusive. In this study, Martini coarse-grained dynamic simulations are performed to characterize the dimerization of palmitoylated CD44 variants in different bilayer environments. CD44 forms homodimer depending on transmembrane domains, and the dimerization efficiency and packing configurations are defected by palmitoylated modifications. In the presence of lipid raft, homodimerization of the palmitoylated CD44 is hardly observed, whereas PIP2 addition compensates to realize dimerization. The results unravel a delicate competitive relationship between PIP2 and palmitoylation in mediating protein homodimerization, which helps to clarify the inside-out signal transduction of CD44 likewise proteins.
Keywords
CD44,Palmitoylated,Homodimerization,Membrane Environments



Comment submit